Choosing the right companies to invest in is one of the primary challenges new stock investors face. Why are company earnings Reports? How do I rate a company? How do I know whether a company is worth investing in? These are some of the questions that one has to ask.
Multiple elements are important in estimating a corporation’s worth, such as its overall historical performance, growth prospects, and management efficiency. One of the absolute key elements of determining whether you should risk your capital with a company is its earnings report.
In this article, you’ll learn what an earnings report is, what you should pay attention to while going over it, and how it can help you make solid data-based investment decisions.
Table of contents:
1. What Are Earnings Reports? What Does a Typical Earnings Report Look Like?
An earnings report is a financial statement that summarizes the financial performance of a given company. The report covers a specific period, usually quarterly or annual. The report details the company’s critical financial metrics, such as its expenses, revenue, and profits. Most Earnings reports will also include the company’s plans and predictions for future performance, which, backed by good-quality data, can be a source of valuable information for the investor.
The format and content of an earnings report may vary depending on the company and the type of report being issued (such as a quarterly or annual report), but rest assured. Most earnings reports are similar.
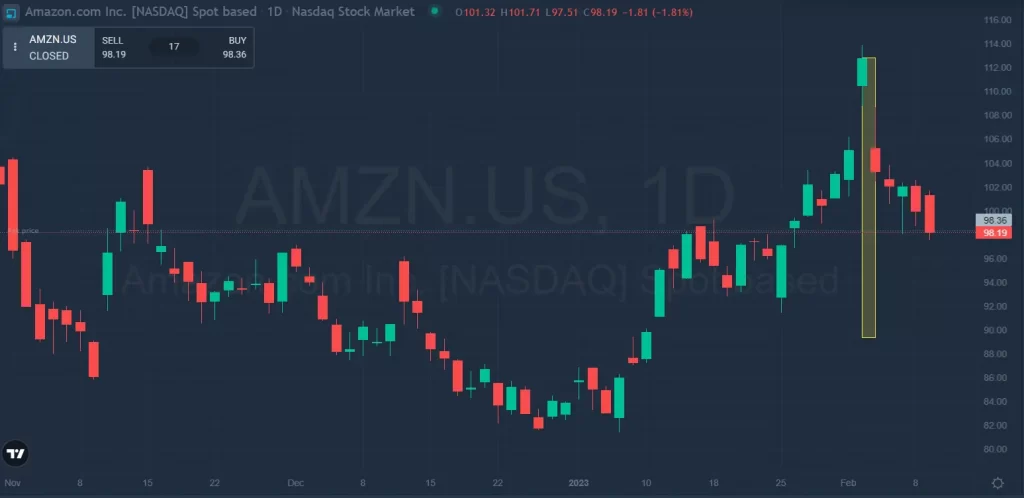
2. Earnings Reports: A Good Source of Financial Performance Indicators
Financial performance indicators (FPIs) help us measure a company’s financial performance. They provide priceless insights into a company’s financial health and help us evaluate its ability to generate profits and grow over time.
Simply put, earnings reports are a great source of condensed information. They provide us with all we need to make a solid, data-driven investment decision.
Earnings reports provide us with invaluable data on corporate earnings that reflect a company’s financial performance and ability to generate profits. As an investor, you will want to use this information to assess the company’s financial health and determine its growth potential before investing.
Read also: How To Build a Stock Trading Strategy?
3. Gaining Insight Into Historical Data for Optimal Investment Decisions
Apart from the data that allows you to make informed investment decisions, you can also use the company earnings reports to compare the financial performances of different companies to ensure you’re getting the best bang for your buck.
What’s more, comparing successive results of earnings reports gives you a unique insight into the company’s historical financial performance. By analyzing data from quarterly or annual reports of different periods, you can determine the general direction in which the company is going.
Corporate earnings reports are extremely important to understand as they can provide priceless data about a company’s financial performance and help you make responsible, data-driven investment decisions.
4. Why Are Company Earnings Reports So Important to Investors?
Company earnings reports are an important piece of the puzzle concerning determining a company’s value. If you are an investor looking to spend your money responsibly and are willing to dig deeper, you will have time to read earnings reports. And here’s why.
5. How Do I Understand Different Earnings Report Components?
Below you will find all the critical components of an earnings report explained simply and with examples. I suggest going through them along with an earnings report of one of the companies you’re looking to invest in to make it more accurate and fun. Ready?
6. What Is Revenue?
Revenue, or the amount of money a company generates, is bound to be present in every earnings report. Revenue is a financial metric that measures the total amount of money a company earns from its sales of goods or services. It is the primary element of a company’s income statement. It represents the income generated from selling products or services before accounting for expenses.
Example:
A company that sells computer software has 1,000 units in its inventory. If the software is priced at $100 per unit, the revenue generated from the sales would be $100,000 (1,000 x $100 = $100,000).
Read also: How to Trade Economic Events. We’ll Let You Know When They Arrive
7. What Is Gross Profit?
To determine a business’s gross profit, one must subtract the cost of goods sold from total revenue. For instance, if a firm’s total revenue is $1,000,000 in a month and the COGS is $600,000, the resulting gross profit would be $400,000 ($1,000,000 – $600,000 = $400,000).
This figure shows the gross profit generated by the business and does not account for operational costs (transportation, salaries, taxes, etc.) Gross profit is a basic indicator of the financial health of the business.
Read also: How to Manage Risk When Trading
8. What Is Net Income?
Net income is the company’s total profit after considering all of its income and expenses, including taxes and other charges. It is one of the critical indicators of a company’s financial health.
Example:
A fashion store has $2,000,000 in sales, $500,000 in operating expenses (including salaries, rent, utilities, and other expenses), and $300,000 in taxes. The net income for this company would be $1,200,000 ($2 000 000 in sales – $500,000 in operating expenses – $300,000 in taxes = $1 200,000).
9. What Are Operating Expenses?
Operating expenses are the costs of day-to-day business activities. They comprise costs related to areas like administrative activities, sales and marketing, human resources, general services, and other operational costs.
Operating expenses are deducted from gross profit to determine the company’s operating profit. Some examples of operating expenses are salaries for administrative employees, office supply costs, marketing and advertising costs, and banking and financial expenses.
10. What Are Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT)?
EBIT is a financial indicator that measures a company’s performance by excluding financial elements such as interest and taxes. It measures the actual profit generated by the company’s operating activities without the effects of financial charges and taxes.
Example:
A tech company has $20,000,000 in revenue. $10,000,000 are operating expenses (including research and development, advertising, and other expenses). In this case, the EBIT for this company is going to be $10,000,000 ($20,000,000 in revenue – $10,000,000 in operating expenses = $10,000,000).
Read also: How to Trade Market Sentiment
11. What Is EPS (Earnings Per Share)?
We calculate earnings per share (EPS) by dividing the overall net income of a given company by the number of its stock’s outstanding shares.
Higher EPS can indicate a corporation’s good health and might suggest that the company is profitable and more likely to pay dividends to its shareholders or invest in growth opportunities. EPS is also widely used to evaluate a company’s performance over a broader time scale and determine its stock value.
Example:
For a company with a net income of $10,000,000 and $10,000,000 outstanding shares of stock, its EPS would be $1. If the company’s net income increased to $15,000,000, but the number of outstanding shares remained the same, the EPS would increase to $1.5 (15 / 10 = 1.5). This would signal that the company’s profitability improved, which could increase its stock value.
Read also: How to Trade Stocks with Little Money Using SimpleFX
12. What Is a Balance Sheet?
A balance sheet is a financial statement that serves as an overview of a company’s financial position. It displays the assets, Equity, and liabilities of that company. Assets are simply the resources available to a corporation that it can use in the future. Liabilities are what the organization owes to others. Equity is the residual interest in the corporation’s assets after deducting liabilities. The balance sheet equation stands as follows: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
13. What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
A cash flow statement shows a company’s cash inflows and outflows over a specified period, most commonly a quarter or a year. It reveals how a company’s operations, investments, and financing activities impact its standing regarding cash. You can use the cash flow statement to assess a company’s capacity for generating positive cash flow, which is one of the key fundamentals for a company’s growth, stability, and health. You can calculate cash flow using this formula: Cash flow = cash inflows – cash outflows.
Example:
The cash flow of that company would be calculated as follows:
Cash flow = $1,000,000 – $800,000 (salaries) – $200,000 (taxes) – $100,000 (marketing) – $50,000 (HR) = $-150,000
This would indicate that the company would have a cash flow of -$150,000. In other words, this company had burned more cash than it generated in that period.
14. What Is Return on Equity (ROE)
Return on Equity (ROE) provides information about a company’s profitability. To do so, it evaluates the amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholder equity. In other words, it represents the shareholders’ returns from their investments.
Return on Equity is calculated using the following formula: ROE = net income/shareholder equity.
Example:
Consider a company with a net income of $100,000 and shareholder equity of $500,000. The ROE would be calculated as follows:
ROE = $100,000 / $500,000 = 0,2 = 20%.
This means that for every $1 of shareholder equity, the company is generating $0.20 in net income. A high ROE indicates the company’s ability to generate stable and high shareholder returns. This means that this company might be a good investment opportunity.
Read also: How to Increase Your Margin Trading Profits with Basic Technical Indicators
15. What Is Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A)?
Management discussion and analysis (MD&A) provides an exhaustive analysis and discussion of the company’s financial and operational performance. The purpose of the MD&A is to provide you with a clear understanding of the company’s financial position, current performance, and future outlook.
The MD&A will help you stay on top of the company’s revenue and earnings trends, shifts in key business drivers, potential risks and uncertainties, and any other relevant events and information affecting the company that management wants investors to be aware of.
16. What Is Market Capitalization (Market Cap?)
A company’s market capitalization (market cap) is another crucial measure of a company’s value as it stands for a company’s total value. Market capitalization is an essential indicator for you as it gives you an idea of the company’s size and potential. To calculate it, you multiply the total number of outstanding shares (all the shares that have been authorized, issued, purchased, and are currently held by investors) of a company’s stock by their current price per share.
Example:
If a company has 1,000,000 outstanding shares and the current price per share is $100, its market capitalization would be $100 million (100 x 1,000,000). A higher market capitalization indicates that the company has a more significant value, while a lower market capitalization may indicate that the company’s value is also low.
17. What Happens When a Company Releases Earnings Reports?
A company’s earnings report can have a lot of sudden and sometimes unforeseeable consequences. It is one of the reasons why companies release not only annual but also quarterly earnings reports. This is also why shareholders generally prefer companies that are either well-established, very transparent, or ideally both.
The results included in an earnings report can have a significant (positive or negative) impact on the company’s stock price and perception.
If the results exceed expectations, the company’s share price will likely rise, sending an optimistic signal to potential investors and shareholders. On the other hand, if the shoe were on the other foot and the earnings report fell short of expectations, the stock price may follow suit resulting in negativity and pessimism among investors, which is a perfect recipe for a decrease in the price of the company’s shares.
Read also: How to Start Trading Stocks: A Quick Starter’s Guide
18. How Company Earnings Reports Impact Investors and Shareholders
Investors, shareholders, financial analysts, and the media examine the company’s earnings and offer opinions on its prospects. Since the market tends to follow the general flow, an inferior earnings report may have detrimental effects on shareholders’ pockets.
An earnings report is regarded as one of the gold-standard sources for evaluating a company’s value. Once released, investors and shareholders will use the data provided to correct the course and make informed investment decisions, such as buying or selling the company’s stock. Furthermore, shareholders use information in earnings reports to evaluate the management and its ability to lead the company and reach financial objectives.
In general, earnings reports are a necessary release for all parties involved. These reports provide essential information about the company’s financial performance, can influence investment decisions and prospects, and are an invaluable resource for investors.
19. How Important Are Earnings Reports to Investors: Summary
Earnings Reports are critical to investors because they provide an overview of a company’s financial performance and growth potential. Earnings, also known as net income or profit, represent the amount of money a company makes after subtracting its expenses from its sales.
Strong company earnings reports suggest stability and growth, making a company more attractive to investors. For example, a company with consistently strong results is more likely to pay dividends to its shareholders. As a result, it provides a steady income stream for investors. In addition, a company with a good earnings history is more likely to see its stock price rise, providing investors with a capital gains opportunity.
20. Corporate Earnings Reports: A Vital Tool for Investors
On the other hand, poor results can signal financial difficulties and lead to a decline in the company’s stock price. For this reason, investors pay close attention to a company’s earnings reports, as they provide valuable information about the company’s financial health and prospects.
Corporate earnings reports play a significant role in investor decision-making, measuring a company’s financial strength and potential for growth and profitability.

